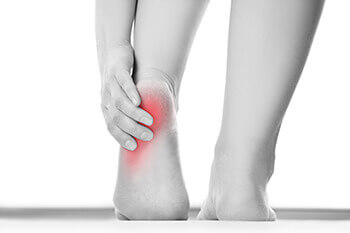
Heel pain is most commonly caused by repetitive stress. With that being said, it may be more common for athletes who perform repetitive movements to be afflicted with heel pain at some point during their activity. Heel pain can occur due to a number of different factors. These may include issues with having poor circulation, complications due to arthritis and diabetes, and poor form when running or exercising, as well as having poor posture.
There are a number of conditions that may also influence pain felt in the heel region. Tarsal tunnel syndrome is one example of a condition that affects the heel. This may occur when the nerve in the back of the foot becomes pinched, thus causing a numbing or tingling feeling as if the heel has pins and needles in them. Heel bursitis is another condition that commonly brings discomfort to the heel. This condition may arise when inflammation occurs at the back of the heel, often occurring due to landing awkwardly or wearing footwear that puts a good amount of pressure on the heel. As a result, the Achilles tendon may swell, causing the pain to increase throughout the day. Simple exercises focused on strengthening the heel and surrounding areas, as well as focused on building the flexibility of the foot, may help to prevent and treat heel pain.
For a proper diagnosis and advised professional treatment plan, we recommend that you consult with a podiatrist as soon as possible to avoid developing a serious condition.
Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) / ESWT
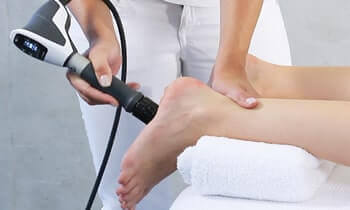
Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) is a new non-invasive treatment that is heralded as the most effective and advanced treatment available that is approved by the FDA. The new technology can generally treat acute or chronic musculoskeletal pain or pain that greatly debilitates mobility or quality of life. Specific areas treatable include:
- Foot and heel pain
- Achilles pain
- Tendon and/or tendon insertion pain
- Neuromas
- Trigger points
Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) revolves primarily around using a particular set of pressure waves that encourages the metabolism, improves blood circulation and speeds up the healing process. In turn, damaged tissue regenerates and heals. As a non-invasive office-based procedure, Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) represents a great advancement in treatment options for a wide range of musculoskeletal conditions.
Expected Results
Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) eliminates pain and restores full mobility, therefore improving quality of life. The benefits of Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) are typically experienced after only 3 treatments. Immediate pain relief is sometimes reported after treatment, though generally pain relief can take up to 4 weeks to begin. Over 80% of patients treated report being pain free and/or experiencing a significant reduction in pain.
Side Effects
Non-invasive Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) has virtually no risks or side effects. In rare cases, patients may experience minor discomfort for a few days. Slight residual pain after intense exercise or a full day of work is normal.
Safety
Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) is safe. The technology is FDA approved and has had extensive clinical studies and tests confirm its safety and efficacy. Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) was originally developed in Europe and is currently in use around the globe. If administered by a qualified professional, Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) has virtually no risks or side effects.
Treatment Duration
Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) treatment sessions take approximately 5-10 minutes. Time depends on the disorder being treated. Generally, 3 treatment sessions are needed at weekly intervals.
Treatment Application
To enhance effectiveness, coupling gel is applied to the treatment area. After applying the gel, Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) pressure waves are released via the applicator which is moved over the area in a circular motion.
Why Consider Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT)
Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) has a proven success rate that is equal to or greater than that of traditional treatment methods (including surgery) and without the risks, complications and prolonged recovery period. Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) is performed in your podiatrist’s office, does not require anesthesia, and requires a minimal amount of time. Patients who use this method can immediately bear weight (i.e. walk) and return to normal activity within a few days of the procedure.
Benefits of Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT)
- Noninvasive
- No anesthesia
- No risk of infection
- No scarring
- No downtime
- Over 80% patient satisfaction
- Faster and easier healing





